华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院下一代互联网接入系统国家工程研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
为保证全光纤电流互感器(FOCT)长期运行的稳定性和可靠性,提出一种在不影响FOCT正常运行的前提下对核心器件关键状态参量如2次谐波幅值、4次谐波幅值、超辐射发光二极管(SLD)光源功率、返回信号功率和调制信号进行实时监测的方法。该方法采用1个分光比为95∶5的2×2耦合器对FOCT的光路进行分光,耦合器一端对SLD发出的光进行监测,另一端对FOCT返回信号进行监测。并通过实际测量与理论结合,验证所提方法对FOCT状态监测的可行性与准确性。结果表明,所提方法能根据FOCT关键状态参量的变化对设备进行综合故障诊断和排查。
全光纤电流互感器 谐波幅值 实时监测 故障预警 激光与光电子学进展
2025, 62(13): 1306008
1 华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院,下一代互联网接入系统国家工程研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
2 湖北光学基础学科研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
3 金银湖实验室,湖北 武汉 430074
针对光纤克尔非线性效应使得无中继系统传输距离增加的限制问题,提出一种基于相位共轭孪生波的无中继非线性补偿优化方案(PCTWO-UT)。该方案在发送端构建共轭双偏振信号,接收端通过相干叠加实现对一阶非线性失真的抵消。相较于传统相位共轭孪生波(PCTW)技术,PCTWO-UT引入训练序列以提升低功率条件下的抗偏振旋转能力,并提出在高色散场景下通过构建链路功率对称性恢复补偿性能的策略。仿真结果表明,该方案在250 km无中继系统中实现了10.8 dB的信噪比提升,此SNR提升相当于系统可承受额外约64 km的链路损耗;引入分布式拉曼放大构建对称功率分布后,60 Gbit/s高速传输下的非线性补偿效率由32%提升至62%。
无中继传输 非线性补偿 相干光通信 相位共轭孪生波 光纤克尔非线性 光学学报
2025, 45(11): 1106004
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Optical and Electronic Information, National Engineering Research Center of Next Generation Internet Access-system, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 PGMF and School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
3 Jinyinhu Laboratory, Wuhan 430048, China
4 Optics Valley Laboratory, Wuhan 430074, China
5 Nanjing Research Institute of Electronic Equipment, Nanjing 210007, China
6 Wenzhou Quality and Technology Testing Research Institute, Wenzhou 325000, China
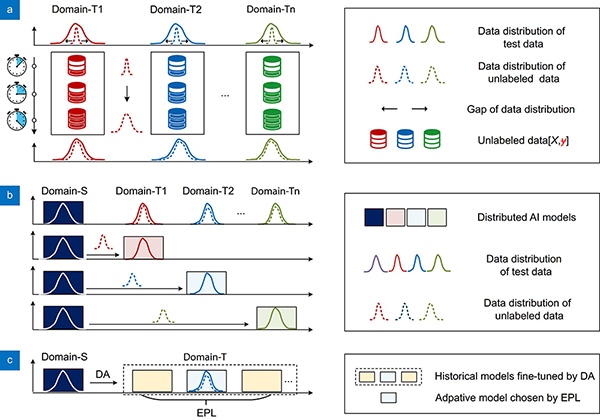
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a critical role in signal recognition of distributed sensor systems (DSS), boosting its applications in multiple monitoring fields. Due to the domain differences between massive sensors in signal acquisition conditions, such as manufacturing process, deployment, and environments, current AI schemes for signal recognition of DSS frequently encounter poor generalization performance. In this paper, an adaptive decentralized artificial intelligence (ADAI) method for signal recognition of DSS is proposed, to improve the entire generalization performance. By fine-tuning pre-trained model with the unlabeled data in each domain, the ADAI scheme can train a series of adaptive AI models for all target domains, significantly reducing the false alarm rate (FAR) and missing alarm rate (MAR) induced by domain differences. The field tests about intrusion signal recognition with distributed optical fiber sensors system demonstrate the efficacy of the ADAI scheme, showcasing a FAR of merely 4.3% and 0%, along with a MAR of only 1.4% and 2.7% within two specific target domains. The ADAI scheme is expected to offer a practical paradigm for signal recognition of DSS in multiple application fields.
artificial intelligence (AI) signal recognition distributed sensor systems (DSS) distributed optical fiber sensors (DOFS) Opto-Electronic Advances
2024, 7(12): 240119
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics (WNLO) and National Engineering Research Center of Next Generation Internet Access System, School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Optics Valley Laboratory, Wuhan 430074, China
3 Department of Electronics and Information Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
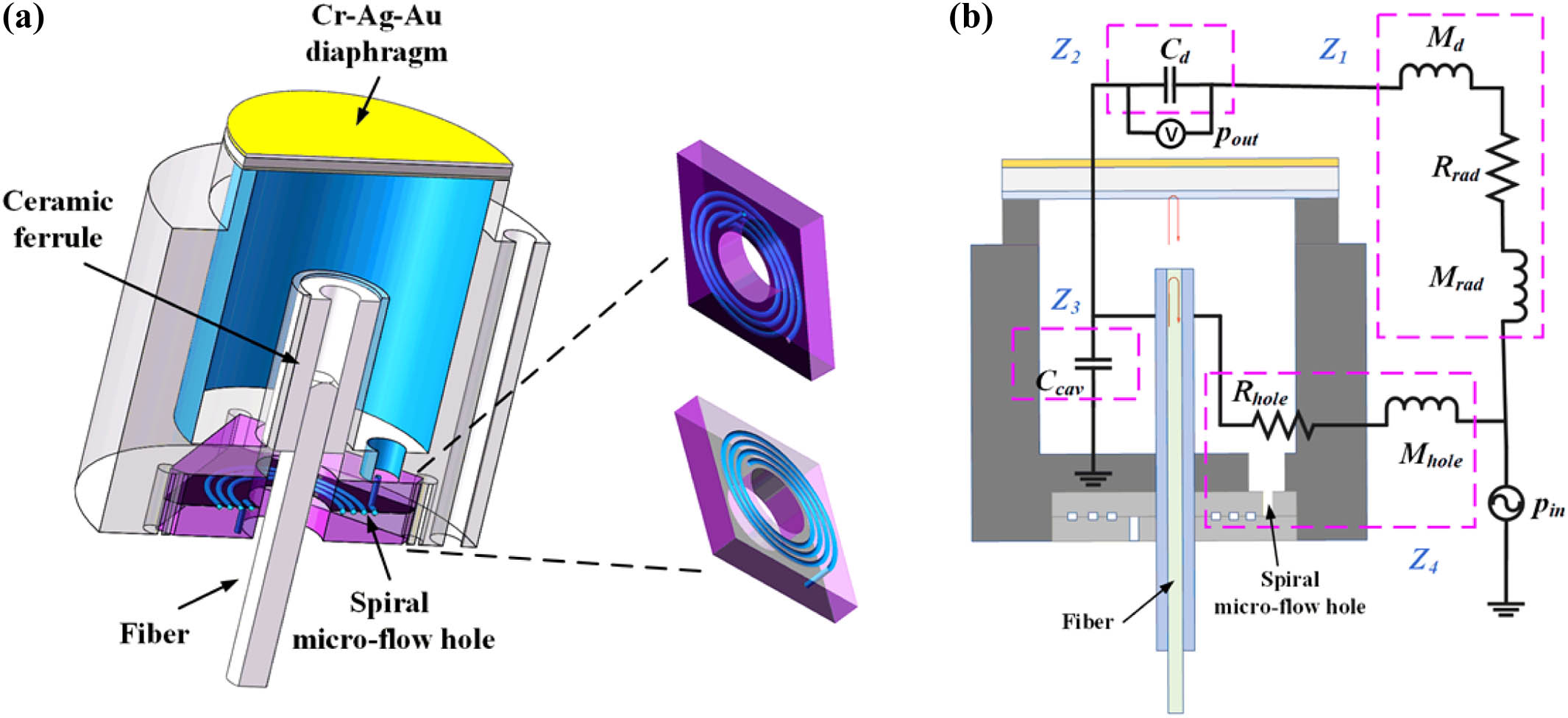
Infrasound detection is important in natural disasters monitoring, military defense, underwater acoustic detection, and other domains. Fiber-optic Fabry–Perot (FP) acoustic sensors have the advantages of small structure size, long-distance detection, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and so on. The size of an FP sensor depends on the transducer diaphragm size and the back cavity volume. However, a small transducer diaphragm size means a low sensitivity. Moreover, a small back cavity volume will increase the low cut-off frequency of the sensor. Hence, it is difficult for fiber-optic FP infrasound sensors to simultaneously achieve miniaturization, high sensitivity, and extremely low detectable frequency. In this work, we proposed and demonstrated a miniaturized and highly sensitive fiber-optic FP sensor for mHz infrasound detection by exploiting a Cr-Ag-Au composite acoustic-optic transducer diaphragm and a MEMS technique-based spiral micro-flow hole. The use of the spiral micro-flow hole as the connecting hole greatly reduced the volume of the sensor and decreased the low-frequency limit, while the back cavity volume was not increased. Combined with the Cr-Ag-Au composite diaphragm, a detection sensitivity of at 5 Hz and a minimum detectable pressure (MDP) of at 5 Hz were achieved. The low detectable frequency can reach 0.01 Hz and the flat response range was 0.01–2500 Hz with a sensitivity fluctuation of . Moreover, the size of the designed sensor was only . These excellent characteristics make the sensor have great practical application prospects.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(5): 969
为了解决热作模具表面磨损并导致失效的问题,基于ANSYS APDL软件,采用数值模拟的方式在热作模具上施加高斯热源,并利用生死单元法将H13合金粉末进行熔覆。通过温度场和应力场对工艺参数进行优化选择,对优化后的工艺参数进行实验验证,并对涂层进行了性能检测。结果表明,所选参数范围内的模拟最优参数为激光功率1200 W,扫描速率12 mm/s,模拟结果与实际涂层的形貌和温度分布较为接近; 数值模拟中的热影响区以及结合区与实验制备的结果高度一致; 测量熔覆层的深度为0.13 mm,与模拟得到的深度为0 mm~0.2 mm相应证,进一步说明了模拟结果的可靠性; 熔覆层的硬度以及耐磨性得到极大的提升,分别是基体的3倍和28倍以上。此研究结果为强化和修复热作模具提供了参考。
激光技术 激光熔覆 数值模拟 温度分布 显微组织 性能分析 laser technique laser cladding numerical simulation temperature distribution microstructure performance analysis

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 HUST-Wuxi Research Institute, Wuxi 214174, China
3 Guangdong Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics Intellisense, Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
4 Optics Valley Laboratory, Wuhan 430074, China
Optical fiber distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) based on phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometry (φ-OTDR) is in great demand in many long-distance application fields, such as railway and pipeline safety monitoring. However, the DAS measurement distance is limited by the transmission loss of optical fiber and ultralow backscattering power. In this paper, a DAS system based on multispan relay amplification is proposed, where the bidirectional erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is designed as a relay module to amplify both the probe light and the backscattering light. In the theoretical noise model, the parameters of our system are carefully analyzed and optimized for a longer sensing distance, including the extinction ratio (ER), span number, span length, and gain of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers. The numerical simulation shows that a bidirectional EDFA relay DAS system can detect signals over 2500 km, as long as the span number is set to be more than 100. To verify the effectiveness of the scheme, a six-span coherent-detection-based DAS system with an optimal design was established, where the cascaded acoustic-optic modulators (AOMs) were used for a high ER of 104 dB. The results demonstrate that the signal at the far end of 300.2 km can be detected and recovered, achieving a high signal-to-noise ratio of 59.6 dB and a high strain resolution of at 50 Hz with a 20 m spatial resolution. This is, to the best of our knowledge, a superior DAS sensing distance with such a high strain resolution.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(6): 968
华中科技大学武汉光电国家研究中心,光学与电子信息学院,湖北 武汉 430074
提出一种基于自外差探测技术的相干光载射频信号传输系统,可以借助自外差探测技术实现光学上变频。在该系统中,4个低频信号被上变频为高频毫米波信号,且在远端射频单元无需进行任何数字信号处理(DSP)。分析了对称边带串扰产生的原因并提出了在发射端消除边带串扰的方法。实验验证了通过在发射端使用4路独立、载频为10 GHz、带宽为1.6 GBaud的16-QAM射频信号和一个载频为20 GHz的单音信号,可以在接收端产生4路独立、载频为30 GHz、带宽为1.6 GBaud的16-QAM毫米波信号。在接收端不使用任何数字补偿算法的情况下,这4路毫米波信号经过50 km标准单模光纤传输后的误差矢量幅度(EVM)值均低于12.5%的阈值,复合速率达到25.6 Gbit/s。此外,发射端的数模转换采样率可以降至24 GSa/s,有效降低了系统的成本和复杂度。
光通信 模拟光载射频 毫米波通信 自外差相干探测 光学上变频 对称边带串扰 中国激光
2022, 49(12): 1206005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Next Generation Internet Access National Engineering Laboratory, School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Yangtze Optical Electronics Co., Ltd. (YOEC), Wuhan 430205, China
With the benefits of low latency, wide transmission bandwidth, and large mode field area, hollow-core antiresonant fiber (HC-ARF) has been a research hotspot in the past decade. In this paper, a hollow core step-index antiresonant fiber (HC-SARF), with stepped refractive indices cladding, is proposed and numerically demonstrated with the benefits of loss reduction and bending improvement. Glass-based capillaries with both high (n = 1.45) and low (as low as n = 1.36) refractive indices layers are introduced and formatted in the cladding air holes. Using the finite element method to perform numerical analysis of the designed fiber, results show that at the laser wavelengths of 980 and 1064 nm, the confinement loss is favorably reduced by about 6 dB/km compared with the conventional uniform cladding HCARF. The bending loss, around 15 cm bending radius of this fiber, is also reduced by 2 dB/km. The cladding air hole radius in this fiber is further investigated to optimize the confinement loss and the mode field diameter with single-mode transmission behavior. This proposed HCSARF has great potential in optical fiber transmission and high energy delivery.
antiresonant fiber (ARF) stepped refractive indices confinement loss bending loss laser pumping Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2021, 14(4): 407–413

Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Optical and Electronic Information and Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Optical fiber sensor network has attracted considerable research interests for geoscience applications. However, the sensor capacity and ultra-low frequency noise limits the sensing performance for geoscience data acquisition. To achieve a high-resolution and lager sensing capacity, a strain sensor network is proposed based on phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer (φ-OTDR) technology and special packaged fiber with scatter enhanced points (SEPs) array. Specifically, an extra identical fiber with SEPs array which is free of strain is used as the reference fiber, for compensating the ultra-low frequency noise in the φ-OTDR system induced by laser source frequency shift and environment temperature change. Moreover, a hysteresis operator based least square support vector machine (LS-SVM) model is introduced to reduce the compensation residual error generated from the thermal hysteresis nonlinearity between the sensing fiber and reference fiber. In the experiment, the strain sensor network possesses a sensing capacity with 55 sensor elements. The phase bias drift with frequency below 0.1 Hz is effectively compensated by LS-SVM based hysteresis model, and the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of a strain vibration at 0.01 Hz greatly increases by 24 dB compared to that of the sensing fiber for direct compensation. The proposed strain sensor network proves a high dynamic resolution of 10.5 pε·Hz-1/2 above 10 Hz, and ultra-low frequency sensing resolution of 166 pε at 0.001 Hz. It is the first reported a large sensing capacity strain sensor network with sub-nε sensing resolution in mHz frequency range, to the best of our knowledge.
optical fiber sensing sensor networking geoscience research quasi-static sensing Opto-Electronic Advances
2021, 4(5): 05200037
华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院下一代互联网接入系统国家工程实验室&武汉光电国家研究中心, 湖北 武汉 430074
分布式光纤布里渊传感器可以测量上百公里光纤上每一点的温度和应变,被应用于桥梁、隧道、输电线路和油气管道等国家重大工程的状态监测。布里渊传感的核心是测量与光纤温度和应变相关的布里渊频移,一般通过测量光纤的布里渊信号谱来得到。布里渊谱的谱线理论上满足洛伦兹线型,其峰值所对应的频率即为布里渊频移。为了降低采样精度和噪声的影响,从布里渊谱中提取布里渊频移最常用的方法是洛伦兹曲线拟合法。然而曲线拟合对初始值敏感,当信噪比较低时,拟合误差显著增加,并且曲线拟合的运算时间较长,降低系统的响应速度。为了提高提取布里渊频移的精度和速度,研究人员采用机器学习算法处理布里渊谱以提取布里渊频移,从而取得比传统拟合算法更好的结果。本文主要介绍近几年机器学习算法在提取布里渊频移中取得的成果,包括奇异值分解、支持向量机和人工神经网络的应用原理和效果。
激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(13): 1306010





